https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/15481
15481번: 그래프와 MST
첫째 줄에 정점의 개수 N과 간선의 개수 M (2 ≤ N ≤ 200,000, N-1 ≤ M ≤ 200,000) 둘째 줄부터 M개의 줄에 간선의 정보 u, v, w가 주어진다. u와 v를 연결하는 간선의 가중치가 w라는 뜻이다. (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109)
www.acmicpc.net
MST 알고리즘 ( prim 알고리즘 사용 ) + LCA 알고리즘을 이용한 문제풀이가 가능하다.
우선 사용될 변수(배열)들은 다음과 같다.
bool visit[MAX_N]; // for mst
int par[MAX_N][21]; // 부모 배열
int dist[MAX_N][21]; // 두노드간의 거리의 최대 간선의 weight가 저장될 배열
int depth[MAX_N]; // for lca
입력된 간선들로 MST를 만들면서 depth, dist, par 배열 완성하게 되면
실제로 MST를 이루는 간선의 갯수는 결국 N - 1 개가 된다.
다음의 예제를 통한 완성 된 결과를 보자
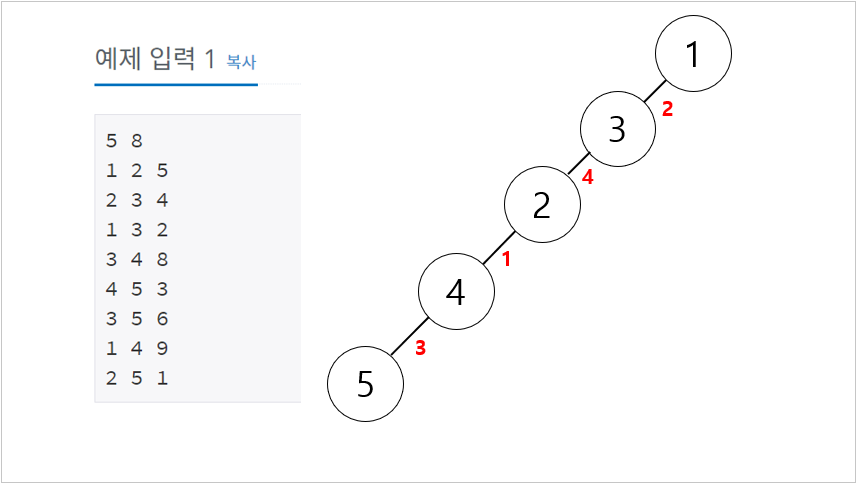
위의 결과로 가장 최선의 MST 는 10 이다
그럼 첫번째 간선에 대해서 확인해보자.
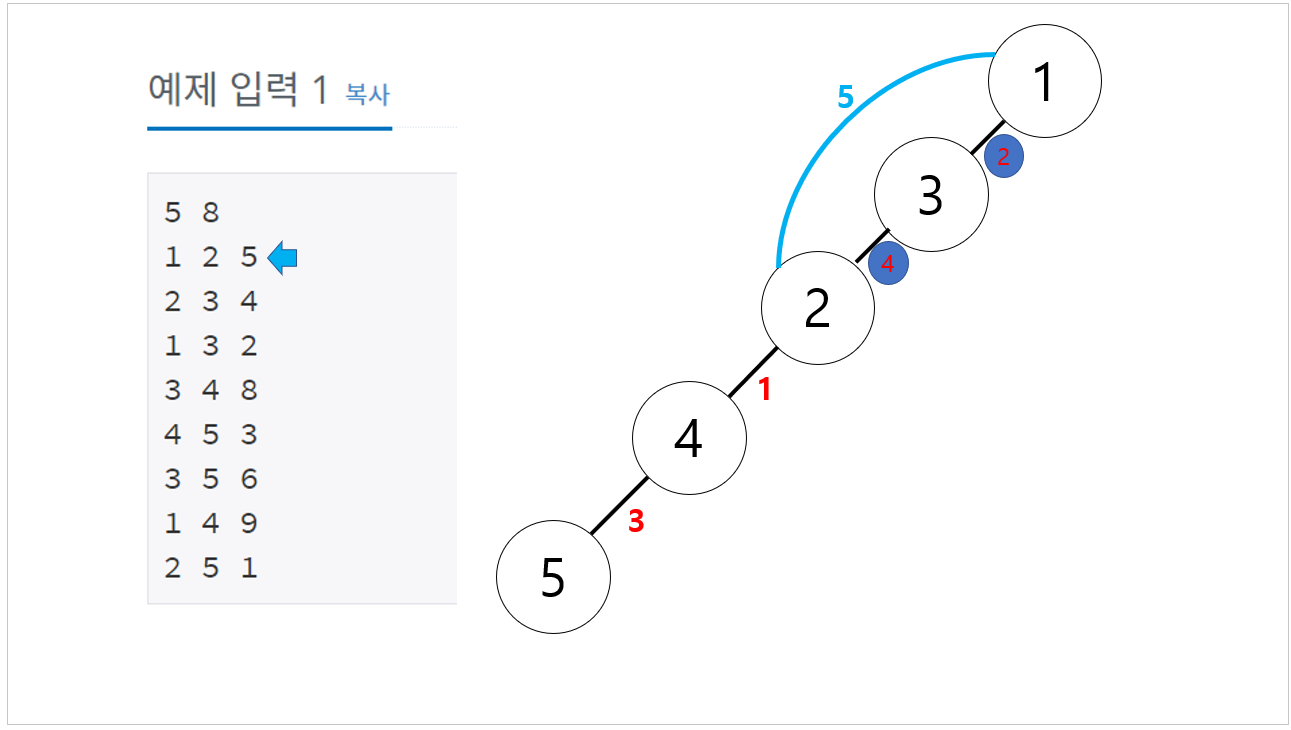
1번과 2번을 이어주게되면
길이 4 또는 2를 제거해야 하는데 당연히 4를 제거 해야 5가 포함된 mst를 완성할 수 있다.
(즉, 1번과 2번노드사이의 최대 길이 경로 하나를 삭제하면 된다 )
다른 케이스를 확인해보자.
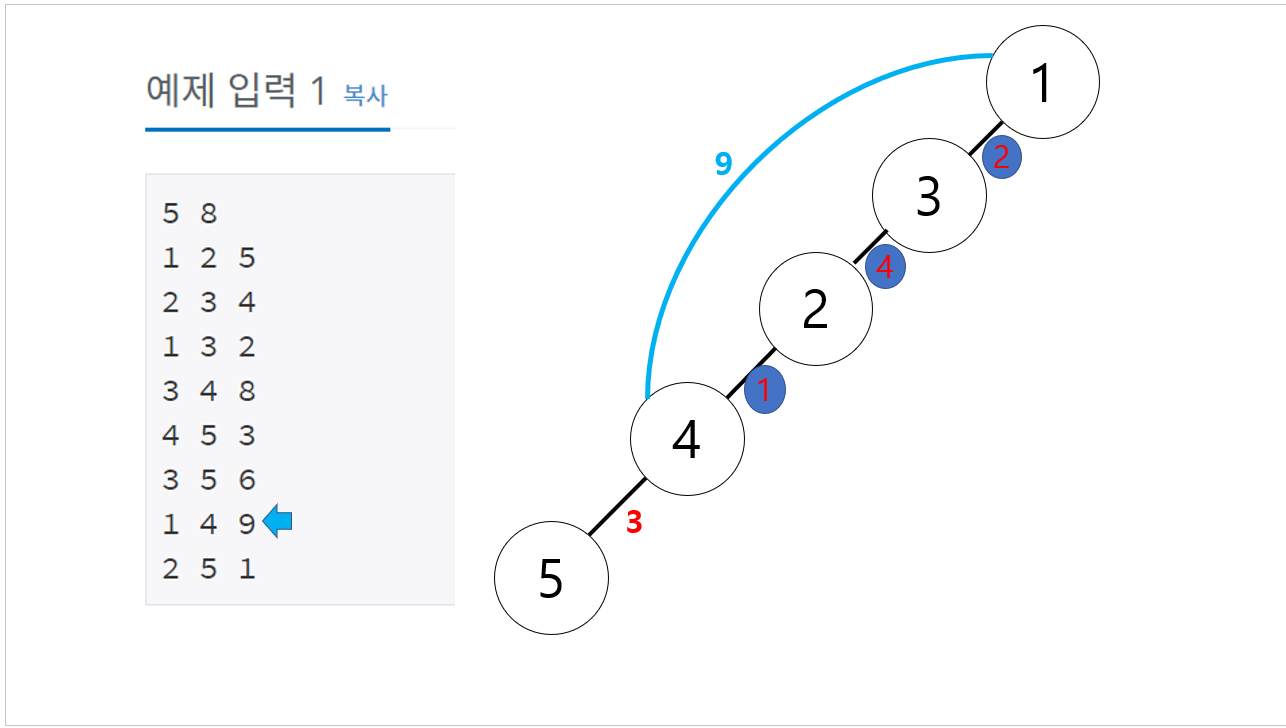
이경우에는 길이 4의 간선을 삭제( 4번노드과 1번노드 사이의 가장 긴 경로의 간선 )
을 하게되면 답이 10( 원래 mst ) - 4 ( 삭제된 간선 ) + 9 ( 삽입된 간선 ) = 15. 이된다.
< 전체 코드 >
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_N 200001
#define swap(a,b) {int t= b ; b = a; a = t;}
// DFS( mst )를 위한 vector
vector<pair<int, int> > map[MAX_N];
// 간선을 순서대로 저장하기위한 클래스
class edge {
public:
int u, v, w;
edge() {}
edge(int u, int v, int w) {
this->u = u;
this->v = v;
this->w = w;
}
};
// 순서대로 저장되어있는 vector
vector<edge> edges;
bool visit[MAX_N]; // for mst
int par[MAX_N][21]; // 부모 배열
int dist[MAX_N][21]; // 두노드간의 거리의 최대 간선의 weight가 저장될 배열
int depth[MAX_N]; // for lca
// pq에 들어갈 item ( cost 순으로 정렬되어 pop 됨 )
class pqItem {
public:
int n, cost, prev, depth;
pqItem() {}
pqItem(int n, int cost, int prev, int depth) {
this->n = n;
this->cost = cost;
this->prev = prev;
this->depth = depth;
}
bool operator > (const pqItem & b) const {
return this->cost > b.cost;
}
bool operator < (const pqItem & b) const {
return this->cost < b.cost;
}
};
// cost 가 제일 작은 것이 pop 됨.
priority_queue< pqItem, vector<pqItem>, greater<> > pq;
// mst 를 돌면서, 부모의 정보와, dist 정보를 저장
long long mst() {
long long ret = 0;
pq.push(pqItem(1, 0,1,0));
while (!pq.empty()) {
pqItem front = pq.top(); pq.pop();
int now = front.n;
int cost = front.cost;
int nowDepth = front.depth;
int prev = front.prev;
if (visit[now]) continue;
visit[now] = true;
ret += cost;
par[now][0] = prev; // 2^0 부모 설정
dist[now][0] = cost; // 2^0 부모까지의 최대 거리 설정
depth[now] = nowDepth; // lca 알고리즘을 위한 depth 설정
for (int i = 0; i < map[now].size(); i++) {
if (visit[map[now][i].first] == false) {
pq.push(pqItem(map[now][i].first, map[now][i].second, now, nowDepth + 1));
}
}
}
return ret;
}
int lca(int x, int y) {
if (depth[x] > depth[y]) swap(x, y);
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
int diff = depth[y] - depth[x];
if (diff >= (1 << i)) {
y = par[y][i];
}
}
if (x == y) return x;
for (int i = 19; i >= 0; i--) {
if (par[x][i] != par[y][i]) {
x = par[x][i];
y = par[y][i];
}
}
return par[x][0];
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
int N, M;
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v >> w;
map[u].push_back({ v,w });
map[v].push_back({ u,w });
edges.push_back( edge(u, v, w) );
}
long long minimum = mst();
for (int i = 1; i <= 19; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
par[j][i] = par[par[j][i - 1]][i - 1];
dist[j][i] = max(dist[j][i-1],dist[par[j][i - 1]][i - 1]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++) {
int u = edges[i].u;
int v = edges[i].v;
int w = edges[i].w;
long long ret = minimum + w;
int lca_node = lca(u, v);
int u_to_lca = depth[u] - depth[lca_node];
int v_to_lca = depth[v] - depth[lca_node];
int maxAns = -1;
for (int j = 19; j >= 0; j--) {
if (u_to_lca >= (1 << j)) {
maxAns = max(maxAns, dist[u][j]);
u_to_lca -= (1 << j);
u = par[u][j];
}
}
for (int j = 19; j >= 0; j--) {
if (v_to_lca >= (1 << j)) {
maxAns = max(maxAns, dist[v][j]);
v_to_lca -= (1 << j);
v = par[v][j];
}
}
cout << ret - maxAns << "\n";
}
}'알고리즘 > [C++]BOJ' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준BOJ] 1626 두 번째로 작은 스패닝 트리 (0) | 2019.10.03 |
|---|---|
| [백준BOJ] 15480_LCA와 쿼리 (0) | 2019.10.03 |
| [백준BOJ] 3176_도로 네트워크 (C++) (0) | 2019.10.02 |